Physical Chemistry
Phase rule
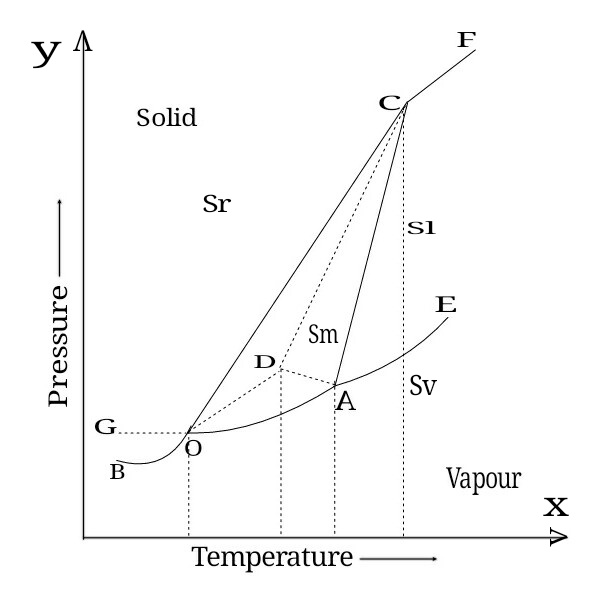
Example- Water System
Phase (P)
Phase is define as homogeneous physically distinct and mechanically separable part of the system.
Component (C)
Minimum number of independent species necessary to define composition of all phases of the system.
Degree of freedom (F)
number of variables such as temperature pressure and concentration taken in consideration and are fixed in order to define the system.
Gibbs Phase Rule
If the equilibrium between the phases is influenced only by temperature pressure and concentration then the degree of freedom related to component and phases of the system is given by
F=C-P+2
Where F- degree of freedom
C- number of components in system
P- number of phases in system
2- variables ( temperature and pressure or temperature and concentration)
When three state of water coexist at a time in equilibrium with each other then phases will be three (P=3) and component will be one (C=1).
If there is equilibrium between three phases then degree of freedom given by
F=C-P+2
F=1-3+2
F=0
Type of systems
Non variant- when F=0
Monovariant- when F=1
Bivariate- when F=2
Trivariant- when F=3

Comments
Post a Comment